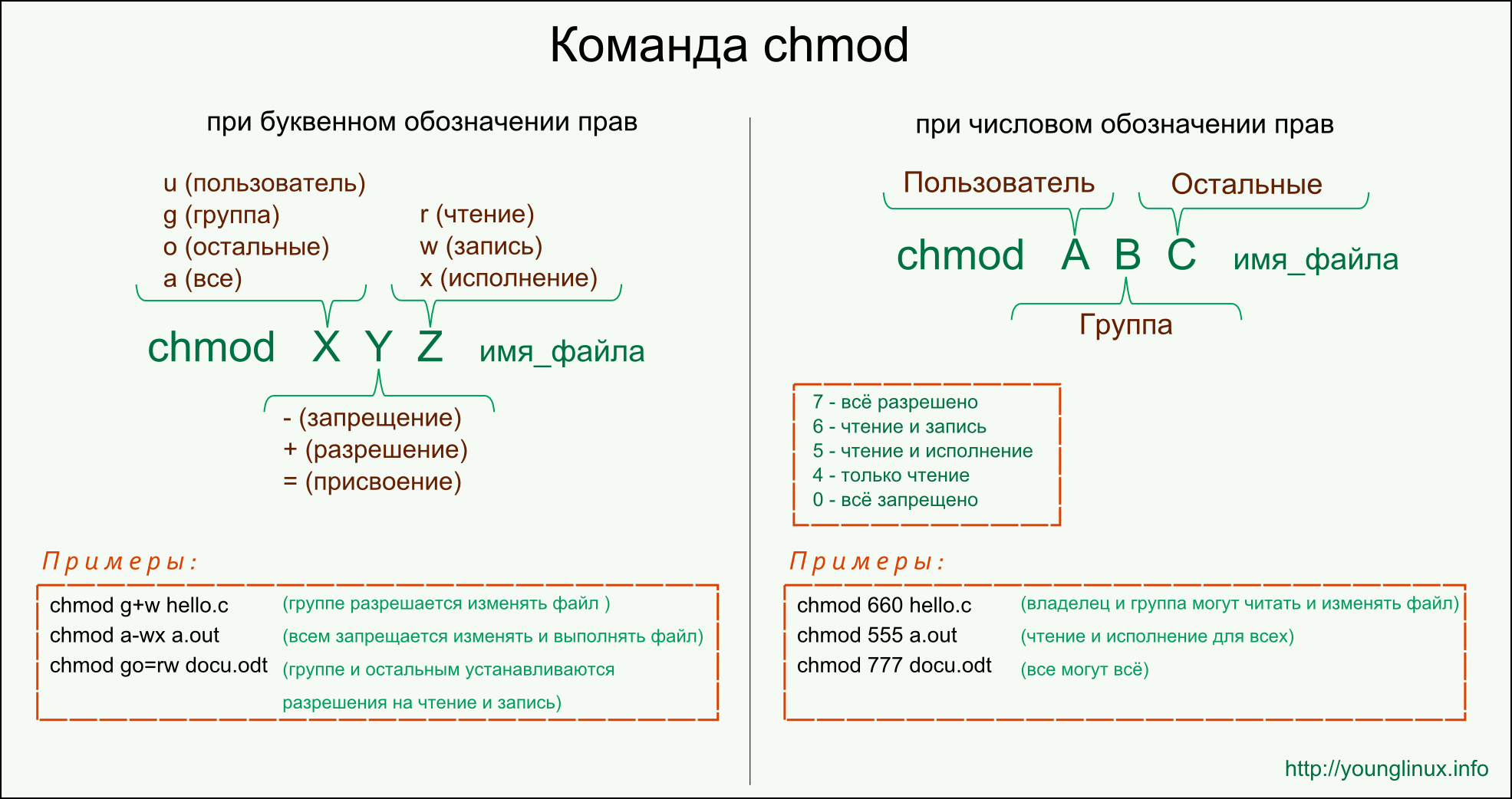
- Disable Performance Counters
- Description
- Change method
- Activation method
- Disable performance counters windows 10
- Чтобы устранить причину появления этого предупреждения
- Performance counters are disabled, they use Exctrlst.exe
- Enable/disable disk performance counters
- Manually rebuild performance counters for Windows Server 2008 64 bit or Windows Server 2008 R2 systems
- Symptoms
- Cause
- Resolution
- Ensure that the counters aren’t disabled in the registry
- Rebuild all performance counters including extensible and third-party counters
Disable Performance Counters
| Data type | Range | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| REG_DWORD | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Description
Enables and disables registry-based performance counters for this service.
If the value of this entry is 1, Perflib does not retrieve performance data about these counters from the registry. As a result, System Monitor, and other tools that use the data, cannot display it. Instead, the tools display a value of 0 or 100%, depending on the counter.
The Performance Library (Perflib) uses this entry to disable counters that cause serious errors. This prevents the troublesome counters from jeopardizing the display of all performance counters on the system. You can use this entry to reenable the counters for a service after the counter DLL has been repaired or replaced.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Enables performance counters for this service. |
| 1 | Disables performance counters for this service. |
Change method
To change the value of this entry, use Extensible Performance Counter List (Exctrlst.exe), a tool on the Windows 2000 Resource Kit CD.
Activation method
To make changes to this entry effective, restart the Remote Registry Service or restart Windows 2000.

This entry only affects the performance counters for a particular service. To enable or disable all registry-based performance counters on the system, add the Disable Performance Counters entry to the Perflib subkey.
To prevent Perflib from disabling counters, set the 0x2 (10) bit in the value of Configuration Flags.

If particular performance counters do not appear in your performance monitoring tool, check the Application Log in Event Viewer for events recorded by Perflib. When Perflib detects disabling errors in a counter DLL, it records an event in the log and sets the value of DisablePerformanceCounters to 1 to disable the counters.

If you set the value of this entry to 1, the performance objects and counters for this service do not appear in any performance tool. You will not be able to use System Monitor, or any tool that uses Performance Library data, to monitor these counters.
Do not edit the registry or use Exctrlst to enable counters that Perflib has disabled, unless the counter DLL has been repaired or replaced. If you do, Perflib will detect the errors and disable the counters again. Or, the troublesome counters can prevent you from monitoring any performance counters on your system.
Disable performance counters windows 10
Дата последнего изменения раздела: 2005-11-18
Анализатор сервера Microsoft® Exchange считывает следующую запись реестра, чтобы определить, отключены ли счетчики производительности логических и физических дисков:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Perfdisk\Performance\Disable Performance Counters
Если анализатор сервера Exchange обнаружит, что значение параметра Disable Performance Counters существует и ему присвоено значение 1, выводится предупреждение.
На сервере, работающем под управлением операционной системы Microsoft Windows®, публикуются счетчики производительности дисков двух типов:
- используемые подсистемой контроля производительности Microsoft Win32® и инструментарием управления Windows (WMI);
используемые старыми приложениями, вызывающими API-интерфейс IOCTL_DISK_PERFORMANCE для получения показаний необработанных счетчиков.
Счетчики производительности, используемые в Win32 и WMI, включаются по умолчанию в системах Microsoft Windows Server™ 2003 и Windows 2000 Server. Необработанные счетчики в обеих операционных системах по умолчанию отключаются. Если параметр реестра Disable Performance Counters, по умолчанию отсутствующий в обеих операционных системах, добавлен и ему присвоено значение 1, счетчики производительности Win32/WMI отключаются, и сбор данных о производительности по этим счетчикам невозможен.
Проще всего отключить счетчики Win32/WMI с помощью программы «Список расширяемых счетчиков» (ExCtrLst.exe). Эта программа с графическим интерфейсом, включенная в наборы ресурсов для Windows 2000 Server и для Windows Server 2003, позволяет администратору выборочно включать и отключать публикацию счетчиков производительности. Когда программа ExCtrLst.exe используется для отключения объекта производительности, она добавляет в реестр элемент Disable Performance Counters и присваивает ему значение 1. Если затем ExCtrLst.exe используется для включения отключенного счетчика, она изменяет значение параметра Disable Performance Counters на 0. (Следует иметь в виду, что при этом элемент Disable Performance Counters не удаляется.)
 Важно! Важно! |
|---|
| Эта статья содержит сведения о редактировании реестра. Перед редактированием реестра убедитесь, что вы знаете, как восстановить реестр в случае возникновения неисправности. Сведения о восстановлении реестра см. в разделе справки «Восстановление реестра» файла Regedit.exe или Regedt32.exe. |
 Чтобы устранить причину появления этого предупреждения
Чтобы устранить причину появления этого предупреждения
Откройте редактор реестра, например, Regedit.exe или Regedt32.exe.
Перейдите к разделу реестра: HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Perfdisk\Performance
В правой области щелкните правой кнопкой мыши параметр Disable Performance Counters и присвойте ему значение 0. Можно также удалить элемент Disable Performance Counters, чтобы вновь включить счетчики.
Закройте редактор реестра и перезапустите все приложения, собирающие данные о производительности, чтобы изменение вступило в силу.
Performance counters are disabled, they use Exctrlst.exe
If you read here, it mean one of my gadgets (System Monitor II, Network Monitor II, Drives Monitor or Top Process Monitor) not work properly. Its connected with a needed counter was missing from the list. This can occur if the counter has been disabled intentionally or if the counter has been disabled by the operating system itself due to it faulting 3 times. When a counter is disabled, a simple registry value is set that tells the OS to ignore it. This value is set under the Performance key of the service in question. If the Disable Performance Counters entry is set to 1 then the counter is disabled, like so:
Now, you can always reenable a performance counter manually by editing the registry, but they are not always easy to find depending on the service name they are listed under. We have a tool that can come in handy in these situations, the Extensible Counter List tool, or Exctrlst.exe. This tool shows a list of all installed performance counters, sorted either by DLL name, service or Counter ID. With this, you can easily see if a counter is enabled or disabled, and set them however you wish. This utility is part of the Windows 2000 resource kit, and can also be downloaded from my site.
Once downloaded, start the installation and follow the installation wizard. The default install location for this will be:
C:\Program Files\Resource Kit or C:\Program Files (x86)\Resource Kit for 64bit OS.
To launch the utility, just double click the executable — Exctrlst.exe.
NOTE: Be sure that you run it under Administrator rights.
When it opens, you should see a window very similar to this:
Now look through the list for the performance counter which you are missing. For System Monitor II and Top Process Monitor it is PersOS, for Network Monitor II it is PerfNet and for Drives Monitor it is PerfDisk. Please don’t forget about TcpIP counter for Network Monitor II. For example, if the disk counters are missing, search for PerfDisk. Once you click the performance counter you are interested in, verify if the Performance Counters Enabled box is checked or not. If the box is not checked, then the performance counter is disabled. To reenable it, all you have to do is place a check mark in the box. The registry change happens immediately, so all you have to do is close the tool when you are done. In case Windows 7 you must restart your computer.
I would also suggest that you have a look at the below articles as well.
Enable/disable disk performance counters
In Microsoft Windows NT and Windows 2000 counters for the objects Logical Disk (partition) and Physical Disk (drive) are disabled by default because a performance hit of a few percent can occur if they are enabled. You must run the diskperf command prior to monitoring disk activity with Performance Monitor and/or Drives Monitor gadget.
Diskperf is included in Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7 and Windows 10 so that it can be used to remotely enable or disable physical or logical disk performance counters on computers running Windows 2000.
To enable the logical entities, at the command prompt, type: diskperf -y
Both Logical and Physical Disk Performance counters on this system are now set to start at boot. In Windows 10 no reboot is required.
The most useful counters for identifying disk bottlenecks are LogicalDisk\Avg Disk Queue Length and PhysicalDisk\Avg Disk Queue Length. (Read more about Disk Queue Length)These counters display the average number of all requests (read and write) that are queued and waiting to be services for the selected disk. If the queue lengths are more than 2 over a long period of time, this could indicate a disk bottleneck. Actually it generally does if the queue length is not the side-effect of a RAM starved system.
To disable the disk counters use command: diskperf -n
To turn on physical disk counters: diskperf -yd
To turn off physical disk counters: diskperf -nd
To turn on logical disk counters: diskperf -yv
To turn off logical disk counters: diskperf -nv
Manually rebuild performance counters for Windows Server 2008 64 bit or Windows Server 2008 R2 systems
This article helps solve an issue where some performance counter libraries become corrupted and need to be rebuilt.
Original product version: В Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: В 2554336
Symptoms
When you use the Performance Monitor tool, some counters may be missing or don’t contain counter data. The performance counter libraries may become corrupted and need to be rebuilt.
You may see the following errors in the application log:
Cause
This behavior may occur if certain extensible counters corrupt the registry, or if Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)-based programs modify the registry.
Resolution
To resolve this issue, use the following methods.
Ensure that the counters aren’t disabled in the registry
The counters may be disabled via registry settings. Check the following registry locations to ensure that the counters haven’t been disabled:
%servicename% represents any service with a performance counter. For example: PerfDisk, PerfOS, etc.
There may be registry keys for DisablePerformanceCounters in any of these locations. As per the article Disable Performance Counters, this value should be set to 0. If the value is anything other than 0 the counter may be disabled.
- A value of 1 means the counter is disabled.
- A value of 2 means the 32-bit counter is disabled.
- A value of 4 means the 64-bit counter is disabled.
Rebuild all performance counters including extensible and third-party counters
To rebuild all performance counters including extensible and third-party counters, type the following commands at an Administrative command prompt. Press ENTER after each command.
Rebuild the counters:
Resync the counters with Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI):
Stop and restart the Performance Logs and Alerts service.
Stop and restart the Windows Management Instrumentation service.
Create a new Data Collector Set (don’t use an existing Data Collector Set).
Sometimes, running lodctr /R may not recover all counters. If you notice this happening, verify the file c:\windows\system32\PerfStringBackup.INI contains the proper information. You can copy this file from an identical machine to restore the counters. There may be slight differences in this file from machine to machine. But if you notice a drastic difference in size, it may be missing information. Always create a backup copy before replacing. There’s no guarantee that copying this file from another machine will restore all counters. If possible, compare the file to backups of the machine to see if the file size has reduced at some point in time.
For many counters, the location of the ini files to install perf counters is under windows\winsxs , such as the ini files for IIS.
If you see the following errors:
You’ll need to use the counter install ini files in the directory c:\Windows\winsxs .
Multiple folders may exist for counters that you need to repair. In those cases, you might need to use trial and error to find the correct ini files.
In this example, try installing the infoctrs.ini from each folder using:
When it’s successful, you’ll see the following entry in the application log:
You need do the same for the following counters:
After which you’ll see:
Following these steps, rerun WINMGMT /RESYNCPERF .
 Чтобы устранить причину появления этого предупреждения
Чтобы устранить причину появления этого предупреждения