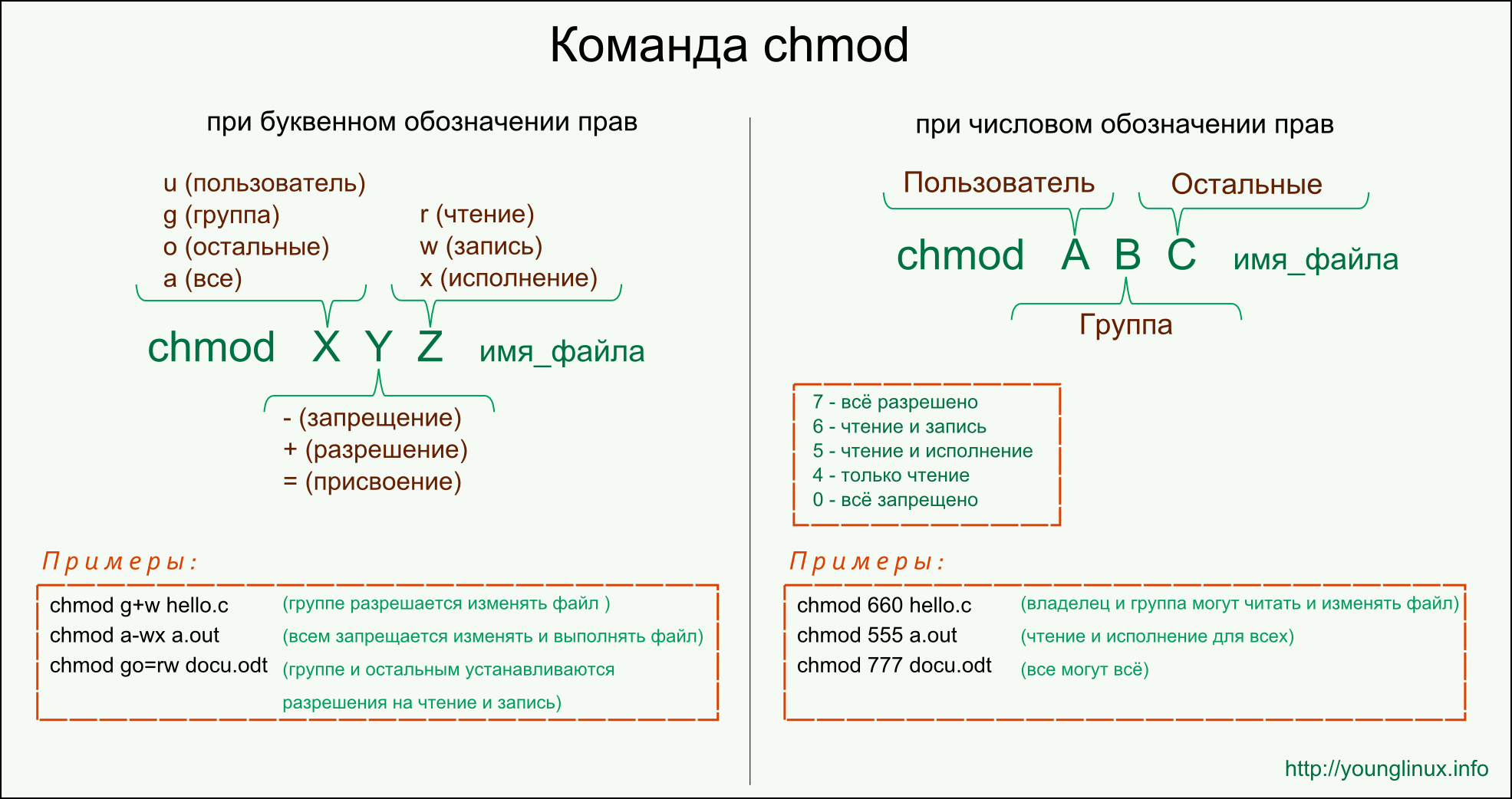
- What are file attributes in Windows?
- File attributes
- File date time
- File Attributes Перечисление
- Определение
- Примеры
- Комментарии
- What are file attributes in windows
- What are File Attributes and What are They Used For?
- Listing of the Commonly Used Attributes
- How to View and Modify attributes?
- Viewing Attributes from Windows Explorer
- Viewing Attributes from DOS prompt
- Conclusion
What are file attributes in Windows?
As you know, computer’s system mostly consists of files, some of them intended for a system, others for a human. To divide from one another and determine system behavior, to each file added some metadata, which known as file attributes. These attributes can have only one of two states: set and clear. The easiest way to change these attributes is to use Attribute Manager. Let’s take a look what kind of attributes are in Windows.
File attributes
From the time of DOS, Microsoft Windows accepted four attributes for files and folders:
- Archive: it indicates that the file has changed since the last backup operation. The file system of the Windows sets this attribute on any file that has changed.
- Hidden: indicates that the file hidden. Windows File Explorer does not show hidden files by default. To make them visible you need to enable the option: «Show hidden files, folders, and drives» in the Control Panel. «Show hidden files, folders, and drives» in the Control Panel.
- System: indicates that it is a critical system file, that is necessary for the computer to operate correctly. Microsoft Windows use it to mark important system files. Windows File Explorer does not show system files by default. To make them visible, you need to disable option: Hide protected operating system files » at the Folder Options dialogue.
- Read-only: indicates that a file should not be modified. File system API usually does not grant write permission to the requesting application, unless the application explicitly requests it. Read-only attributes on folders typically ignored.
As new versions of Windows came out, Microsoft has introduced new file system NTFS and subsequently NTFS5, which has some new attributes:
- Compressed: When set, Windows compresses the file. The best use of compression is for files that are repetitive, seldom written, usually accessed sequentially, and not themselves compressed. Log files are an ideal example.
- Encrypted: When set, Windows encrypts the file to prevent unauthorized access. Encrypting File System provides secure and user-transparent encryption of any file or folder on a NTFS volume.
- Indexed: When set, Indexing Service or Windows Search do not include the file in their indexing operation.
- Sparse file: Indicates that the file is sparse. Sparse file attempts to use file system space more efficiently when blocks allocated to the file are mostly empty. Achieved by writing brief information representing the empty blocks to disk instead of the actual «empty» space which makes up the block, using less disk space.
- Temporary: A file that used for temporary storage. File systems avoid writing data back to mass storage if sufficient cache memory is available, because typically, an application deletes a temporary file after the handle is closed.
- Offline: The data of a file is not available immediately. This attribute indicates that the file data physically moved to offline storage. Attribute used by Remote Storage, which is the hierarchical storage management software.
File date time
Every file or folder has the date and time information about its creation, access and modify.
- Creation Time: the date and time the file or directory created.
- Last Access Time: the date and time the file or directory was last accessed. The last access time includes the last time the file or directory was written to, read from, or, in the case of executable files, run.
- Last Write Time: the date and time the file or directory was last written to, truncated, or overwritten. This date and time are not updated when file attributes or security descriptors changed.
File Attributes Перечисление
Определение
Предоставляет атрибуты для файлов и каталогов. Provides attributes for files and directories.
Это перечисление имеет атрибут FlagsAttribute, который разрешает побитовое сочетание значений его элементов.
Этот файл помечается для включения в операцию добавочного резервного копирования. This file is marked to be included in incremental backup operation. Windows устанавливает этот атрибут при каждом изменении файла, и программному обеспечению резервного копирования нужно снимать его при обработке файла в рамках добавочного резервного копирования. Windows sets this attribute whenever the file is modified, and backup software should clear it when processing the file during incremental backup.
Файл сжат. The file is compressed.
Зарезервировано для будущего использования. Reserved for future use.
Файл является каталогом. The file is a directory. Directory поддерживается в Windows, Linux и macOS. Directory is supported on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Файл или каталог зашифрован. The file or directory is encrypted. Для файла это означает, что все данные в файле зашифрованы. For a file, this means that all data in the file is encrypted. Для каталога это означает, что шифрование производится по умолчанию для вновь создаваемых файлов и каталогов. For a directory, this means that encryption is the default for newly created files and directories.
Файл скрытый и, таким образом, не включается в обычный список каталога. The file is hidden, and thus is not included in an ordinary directory listing. Hidden поддерживается в Windows, Linux и macOS. Hidden is supported on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Файл или каталог включает поддержку целостности данных. The file or directory includes data integrity support. Когда это значение применяется к файлу, все потоки данных в этом файле имеют поддержку целостности. When this value is applied to a file, all data streams in the file have integrity support. Когда это значение применяется к каталогу, все новые файлы и подкаталоги этого каталога по умолчанию включают поддержку целостности. When this value is applied to a directory, all new files and subdirectories within that directory, by default, include integrity support.
Файл является стандартным файлом без специальных атрибутов. The file is a standard file that has no special attributes. Этот атрибут действителен, только если он используется отдельно. This attribute is valid only if it is used alone. Normal поддерживается в Windows, Linux и macOS. Normal is supported on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Файл или каталог исключен из проверки целостности данных. The file or directory is excluded from the data integrity scan. Когда это значение применяется к каталогу, по умолчанию для всех новых файлов и подкаталогов этого каталога поддержка целостности исключается. When this value is applied to a directory, by default, all new files and subdirectories within that directory are excluded from data integrity.
Файл не будет индексироваться службой индексирования содержимого операционной системы. The file will not be indexed by the operating system’s content indexing service.
Файл находится в автономном режиме. The file is offline. Данные этого файла недоступны непосредственно. The data of the file is not immediately available.
Файл доступен только для чтения. The file is read-only. ReadOnly поддерживается в Windows, Linux и macOS. ReadOnly is supported on Windows, Linux, and macOS. В Linux и macOS изменение флага ReadOnly — это операция с разрешениями. On Linux and macOS, changing the ReadOnly flag is a permissions operation.
Файл содержит точку повторной обработки, блокирующую определяемые пользователем данные, связанные с файлом или каталогом. The file contains a reparse point, which is a block of user-defined data associated with a file or a directory. ReparsePoint поддерживается в Windows, Linux и macOS. ReparsePoint is supported on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Файл является разреженным. The file is a sparse file. Разреженными файлами обычно являются большие файлы, в которых содержатся в основном нулевые данные. Sparse files are typically large files whose data consists of mostly zeros.
Файл является системным. The file is a system file. То есть файл является частью операционной системы или используется исключительно операционной системой. That is, the file is part of the operating system or is used exclusively by the operating system.
Файл является временным. The file is temporary. Временный файл содержит данные, необходимые во время выполнения приложения, но не требуемые после завершения приложения. A temporary file contains data that is needed while an application is executing but is not needed after the application is finished. Файловые системы для ускорения доступа стремятся держать все данные в памяти, а не сбрасывать их обратно на запоминающее устройство. File systems try to keep all the data in memory for quicker access rather than flushing the data back to mass storage. Приложение должно стереть временный файл сразу после того, как он перестанет быть нужным. A temporary file should be deleted by the application as soon as it is no longer needed.
Примеры
В следующем примере показано, как получить атрибуты для файла и проверить, доступен ли файл только для чтения. The following example shows how to retrieve the attributes for a file and check if the file is read-only.
Комментарии
Вы можете получить атрибуты для файлов и каталогов, вызвав File.GetAttributes метод, и вы можете задать их, вызвав File.SetAttributes метод. You can get attributes for files and directories by calling the File.GetAttributes method, and you can set them by calling the File.SetAttributes method.
Невозможно изменить состояние сжатия File объекта с помощью File.SetAttributes метода. It is not possible to change the compression status of a File object by using the File.SetAttributes method. Вместо этого необходимо сжать файл с помощью средства сжатия или одного из классов в System.IO.Compression пространстве имен. Instead, you must actually compress the file using either a compression tool or one of the classes in the System.IO.Compression namespace.
Следующие атрибуты не поддерживаются .NET Core в Linux и macOS: The following attributes are not supported by .NET Core on Linux and macOS:
What are file attributes in windows
We use digital files every day, but it’s relatively rare we need to recognize the attributes of a digital file. This article is all about understanding File Attributes in Windows.
You might for example have wondered how the Windows operating system differentiates files that are visible from those that are hidden. Or let’s say a text editor program pops up an error message informing you the file is “read-only” when you’re trying to save changes to the file — you might ask yourself: how does the text editor know that the file is read-only? File Attributes tag files with additional information that Windows uses to act on.
Knowing a little about File Attributes will help you understand why certain things happen with files, and why certain things can’t happen if an attribute is defined in a certain way.
What are File Attributes and What are They Used For?
File attributes are pieces of information associated with every file and directory that includes additional data about the file itself or its contents. They can exist in only one of two states – Set or Cleared; like an On or Off state. Attributes can be in files, directories, volumes and certain system objects. They are used by the operating system and software applications to define file system behavior.
Listing of the Commonly Used Attributes
A byte stores the attributes of a file, with each specific attribute assigned to a bit of a byte. To enable a certain attribute, the system will assign a ‘one’ to the corresponding bit, which represents the ‘On’ state. (These are referred to as flagging or setting the attribute). A Windows operating system (Win32) stores the file attributes as 32-bit quantity, while the original MS-DOS file attributes only have 8 bits to store file attributes.
Below are the common attributes and the bits that represent them:
Not Content Indexed (I)
A file may have more than one attribute mapped to it by adding the bits to form the byte attribute. A read-only, hidden directory would have the attribute byte of 00010011, a result of the three attributes added together. Below are the descriptions of each attribute:
- Read-Only (R) : Read-Only attribute will prevent software programs from saving changes to a file. This is useful if you want to write protect a file. Note that a Read-Only file will not prevent it from being deleted.
- Hidden (H) : A file marked with the hidden attribute will be hidden from view under normal viewing conditions.
- System (S) : A file or directory used exclusively by the operating system which should not be altered or deleted.
- Directory (D) : This attribute is tagged to folders or sub-folders to differentiate them from files.
- Archive (A) : This bit is used by software applications that modify files as well as backup software as a “communication link”. Some PC backup software (for example SyncBackPro and SyncBackSE) allows incremental backups by the user, which only backs up files that have changed since the previous backup. When the backup software archives or backs up the file, it resets the archive bit (tagging it zero or Off). Any software that subsequently make changes to the file is expected to set the archive bit. Thus, when the backup software runs the next time, it will be able to identify the modified files by analyzing the archive bits, and backs up those files with the modified bits.
Note that certain programs may modify the files without marking the archive attribute. If the backup software uses incremental backups to backup these files, it will rely on the software to set the bit appropriately. It is therefore important to note that you should not rely solely on this setting to ensure critical files are backed up.
Not Content Indexed (I) : Windows has a search function which indexes all the files and directories in the drive in order to achieve faster results. By default, this attribute is not set, thereby allowing the operating system to include the file into the indexing list. A user could choose to opt out certain files by setting this attribute to On . When set, Windows will skip files that have this option checked.
How to View and Modify attributes?
There are a few ways to view and change attributes. Two of them are via the file or folder properties from Windows Explorer or using the ATTRIB command from MS-DOS prompt (type CMD command to bring up the DOS window).
Viewing Attributes from Windows Explorer
Right-clicking and selecting Properties on any file or folder in Windows Explorer will bring up the Properties window, which shows the attributes of the selected item.
Note: The extended attributes (compress and encrypt) will not be shown when you use the ATTRIB command. However, you can view these attributes by executing the Compact and Cipher commands, respectively.
Viewing Attributes from DOS prompt
To view attributes, you can type ATTRIB command from the DOS prompt.
Typing ATTRIB /? will bring up a list of all the syntax available to query a file.
To view what attributes are assigned to a file, type the following:
From here, we can see that the TEST.TXT file has the Archive, Hidden and Read-Only attribute enabled (A, H & R are shown).
Using the ATTRIB command allows a user to Set or Clear an attribute of a file. For the above example, if we wish to remove the attribute of Hide and Read-Only from the file, we could type:
ATTRIB -H -R C:\FOLDER\TEST.TXT
The example above shows that the hidden and Read-Only attribute have been removed from TEST.TXT.
Conclusion
This article has hopefully helped you understand a little more about Windows file attributes. Being familiar with file attributes will help you better understand how the file system works in a Windows environment. You could use this knowledge to your advantage by selecting the Fast Backup (scanning the Archive Attribute) option in SyncBackSE and SyncBackPro to greatly reduce the time needed for each backup, thereby increasing your productivity and freeing up your system resources for other tasks.