- Проблемы с выделением больших объёмов памяти
- Проблемы с выделением больших объёмов памяти
- Отзывы о программе MemTest
- What is the RAM Limit in Windows 10 in 2018?
- RAM Limit in Windows 10, Windows 8.1
- Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
- Memory and Address Space Limits
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Vista
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home Server
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Embedded
- How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits
Проблемы с выделением больших объёмов памяти
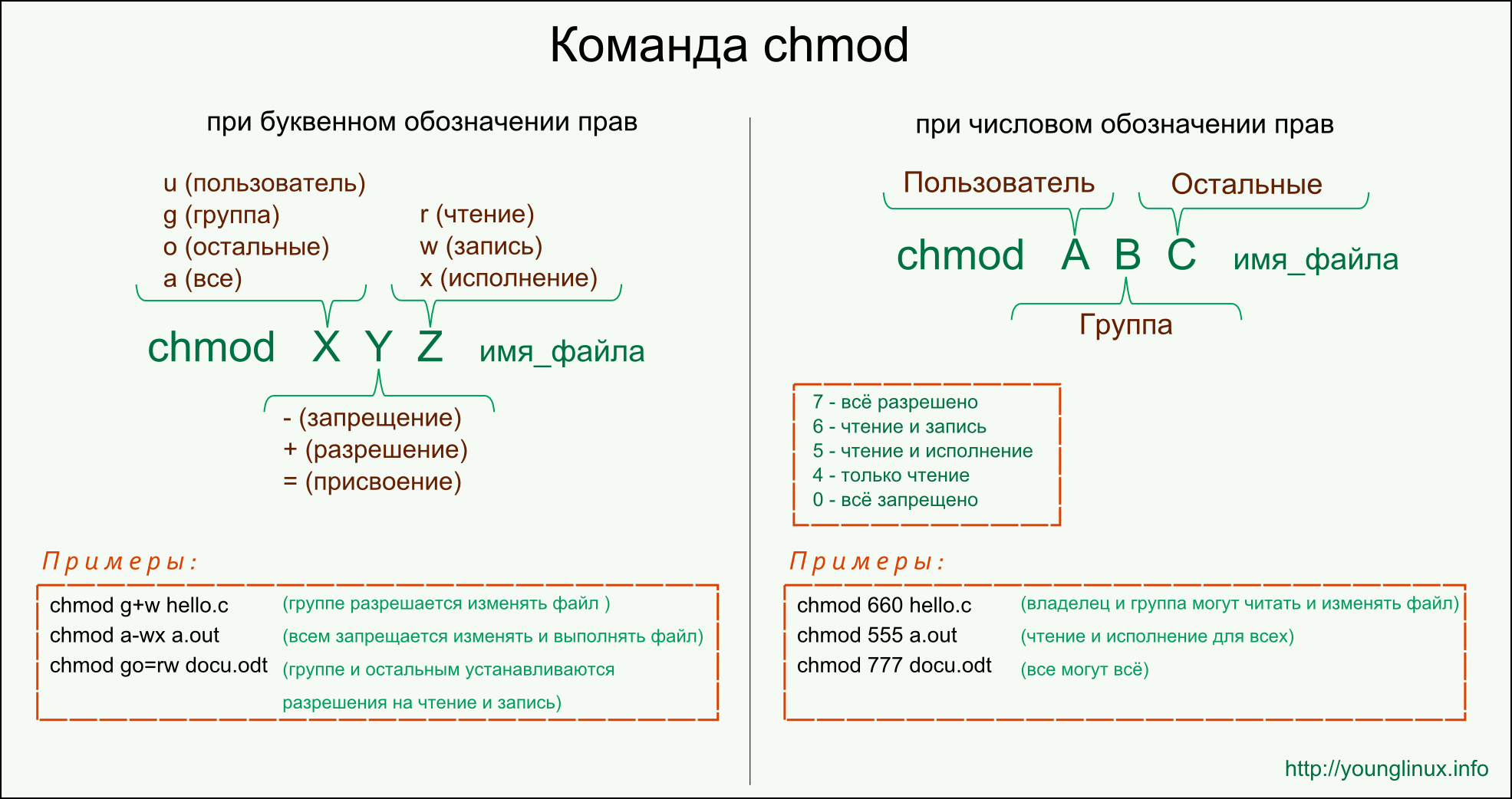
Что делаем:
Выделяю память самописным dummy вектором, который раздувается вдвое, когда нужно.
Что получаем:
Система сложная, минимальный код вычленять не пробовал, но падает где-то на очередной попытке раздуться с std::bad_alloc. Что характерно, памяти, вроде, достаточно: process explorer показывает
600Mb virtual memory, то есть даже если вся память процесса раздуется вдвое, то ещё места будет достаточно.
Вопрос:
что делать? куда копать?
//upd: что особенно удивительно, раз на раз не приходится и при детерменированной стратегии использования памяти приложение то падает, то нет.
NULL_PTR
ну я наталкивал везде free(malloc(10)); вроде не падало. если я побил память, почему тогда еггог не проявляется при меньших запросах памяти? вообще маловероятно, хотя и не исключено.
А если количество используемой памяти определять не эксплорером, а своей программой?
Можно же при каждом перевыделении писать в лог-файл.
andriano
> Можно же при каждом перевыделении писать в лог-файл.
не хочу
короче ещё поанализировал код. программа падает, когда использует памяти порядка 700Mb. особенность самопального вектора в том, что когда раздувается, он создаёт копию данных в два раза большего размера, копирует в них старые данные, старые данные удаляет. может, баг в том, в определённый момент в системе хранится не n, не 2 * n памяти a n + 2 * n, то есть 700 * 3
2,1Gb, то есть впритык? ну это было бы несколько странно, потому что векторов несколько и размеры у них примерно одинаковые, то есть все разом они занять в три раза больший размер вроде не могут
Suslik
Посмотри, что покажет VMMap.
Проблемы с выделением больших объёмов памяти
Что делаем:
Выделяю память самописным dummy вектором, который раздувается вдвое, когда нужно.
Что получаем:
Система сложная, минимальный код вычленять не пробовал, но падает где-то на очередной попытке раздуться с std::bad_alloc. Что характерно, памяти, вроде, достаточно: process explorer показывает
600Mb virtual memory, то есть даже если вся память процесса раздуется вдвое, то ещё места будет достаточно.
Вопрос:
что делать? куда копать?
//upd: что особенно удивительно, раз на раз не приходится и при детерменированной стратегии использования памяти приложение то падает, то нет.
NULL_PTR
ну я наталкивал везде free(malloc(10)); вроде не падало. если я побил память, почему тогда еггог не проявляется при меньших запросах памяти? вообще маловероятно, хотя и не исключено.
А если количество используемой памяти определять не эксплорером, а своей программой?
Можно же при каждом перевыделении писать в лог-файл.
andriano
> Можно же при каждом перевыделении писать в лог-файл.
не хочу
короче ещё поанализировал код. программа падает, когда использует памяти порядка 700Mb. особенность самопального вектора в том, что когда раздувается, он создаёт копию данных в два раза большего размера, копирует в них старые данные, старые данные удаляет. может, баг в том, в определённый момент в системе хранится не n, не 2 * n памяти a n + 2 * n, то есть 700 * 3
2,1Gb, то есть впритык? ну это было бы несколько странно, потому что векторов несколько и размеры у них примерно одинаковые, то есть все разом они занять в три раза больший размер вроде не могут
Suslik
Посмотри, что покажет VMMap.
Отзывы о программе MemTest
| Загрузок всего | 460 063 |
| Загрузок за сегодня | 31 |
| Кол-во комментариев | 20 |
| Подписавшихся на новости о программе | 12 (подписаться) |
Anjey про MemTest 7.0 [30-05-2020]
Ну во первых это не установочный файл, то бишь скачиваем не программу а .
во вторых — WINRAR при открытии файла пишет следующее:
«WinRAR не бесплатная программа. По окончании 40 испытательного периода Вы должны купить лицензию .
И это называется бесплатное скачивание?
3 | 32 | Ответить
West в ответ Anjey про MemTest 7.0 [30-05-2020]
То, что ты пользуешься условно-бесплатным архиватором это твои проблемы!! При чем тут вообще WinRar до MemTest.
Я тебе по большому секрету скажу, что архивы можно открыть не только винраром. Есть бесплатный 7-zip.
И да, это называется бесплатным скачиванием.
Ты с какого дерева слез?
31 | 3 | Ответить
Gvidas про MemTest 6.3 [26-09-2019]
Admin в ответ Gvidas про MemTest 6.3 [25-11-2019]
Проверено — вирусов НЕТ!
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/url/cc0aada804f44e46274732950c8341d4a36ea66e4a3f8d9133c86e1ab0e272a8/detection
5 | 7 | Ответить
sаN4es про MemTest 6.0 [17-04-2019]
Nopost про MemTest 6.0 [22-01-2018]
Windows limits the amount of contigous RAM MemTests can allocate to betwen 2 and 3,5GB.
To test all your RAM, run more than one copy of MemTest simultaneously and set each copy to test a portion of available RAM. Running more than one copy of MemTest does not lower the qualyty of the test (and can even improve it if you have multiple cores or CPUs)
NOTE: this process in automated in MemTest Pro
Машинный перевод:
Windows ограничивает количество смежных RAM MemTests, которые можно распределить между 2 и 3,5 ГБ.
Чтобы протестировать всю оперативную память, одновременно запускайте несколько экземпляров MemTest и установите каждую копию для проверки части доступной оперативной памяти. Запуск более чем одной копии MemTest не снижает квалификацию теста (и может даже улучшить его, если у вас несколько ядер или процессоров)
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Этот процесс в автоматизированном виде в MemTest Pro
И ещё:
.If you find this free version useful, please considering purchasing the PRO [$5] or Deluxe [$14] versions, which add additional features.
Если вы найдете эту бесплатную версию полезной, подумайте о покупке версий PRO [$ 5] или Deluxe [$ 14], которые добавят дополнительные функции.
10 | 38 | Ответить
Знаток про MemTest 6.0 [18-11-2017]
Я хочу предупредить,эту программу «MemTest6.0» не путайте с программой «Memtest86 7.4» (которая работает до загрузки системы)от PassMark SoftWare http://www.softportal.com/software-30821-memtest86.html (снимки экрана от версии 4.1, образ это программы версии 4.1 скачал с другого сайта, энтеркомпьютер)
8 | 17 | Ответить
iBot про MemTest 5.1 [29-08-2017]
Знаю эту программу лет 5 или больше. Единственная, которая показывала ошибки на старой системе, там возникла ситуация несовместимости старых и новых планок памяти (докупил), они отказывались работать на CR1 (синие экраны, спонтанные вылеты на ровном месте). При этом я знал, что старые планки железно стабильные, ведь до покупки новых проблем не было. Ни тест оперативной средствами Windows ни memtest86 ничего не показывали (может мало прогонов делал), а эта показала сразу. Когда выставил CR2 проблема исчезла, как и ошибки из этой программы теста. Я даже Pro версию купил, после той вакханалии, как спасибо разработчику.
Сейчас обновил систему и эта программа снова выручила. Разогнал Ryzen в АИДЕ64 15 часов стабилен (CPU+FPU+Cache), а вот в одном из 3-х инстансов этой программы по 2000 возникло две ошибки на 200+%, в оcтальных 1500% чисто. Запустил memtest86 7.4 тот подтвердил на первом проходе в 7 тесте единственную ошибку. Сделал еще 4 прохода, в одном снова появилась одинокая ошибка в 7 тесте. Программа работает как надо и memtest86 это подтвердил в этот раз.
Запускайте число инстансов на половину или 2/3 вашей памяти, оставляйте на ночь. Если не найдет ошибок, значит у вас все на 99,99999999% гуд.
5 | 11 | Ответить
Дмитрий про MemTest 5.0 [28-01-2017]
У кого не получается, пробуйте тестить по одной планке.
5 | 6 | Ответить
aleks про MemTest 5.0 [26-01-2017]
What is the RAM Limit in Windows 10 in 2018?
If you were wondering what the RAM limit is in Windows 10, Windows 8.1, read below to find the simple answer to this question. 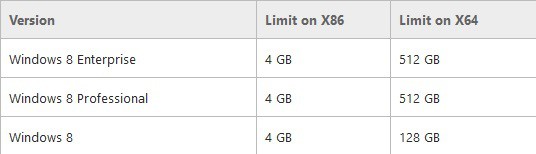
On the other hand, many expected Windows 10 to support even more RAM power since the OS brings some heavy apps to the table — such as Mixed Reality apps. The RAM limit on Windows 10 has indeed increased, reaching 2TB GB for Windows 10 Pro and Windows 10 Enterprise.
RAM Limit in Windows 10, Windows 8.1
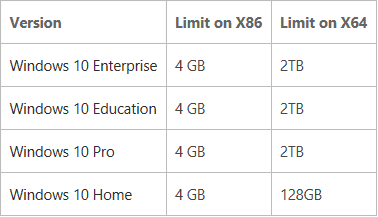
You can see in the above image, the maximum physical memory RAM limits for Windows 10, Windows 8 which are the same for Windows 8.1, as well. They are as follows:
- RAM limits in Windows 10, Windows 8.1 Enterprise – 4GB on x86, 512GB on x64
- RAM limits in Windows 10, Windows 8.1 Professional – 4GB on x86, 512GB on x64
- RAM limits in Windows 10, Windows 8.1 – 4GB on x86, 128GB on x64
The screenshot below lists the RAM limit for Windows 10:
You also need to be careful at this official explanation related to how graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits:
Devices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions.
Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can.X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the “lost” memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk.
Unfortunately, although Windows 10 supports more RAM, sometimes computers can’t access all of it. If you’re experiencing the same problem, check out this guide to learn what you can do if Windows 10 won’t read all RAM.
What about you – are you running a monster of a machine on your device? What is your RAM limit in Windows 10, Windows 8 and Windows 8.1?
RELATED STORIES TO CHECK OUT:
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases.
Limits on memory and address space vary by platform, operating system, and by whether the IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE value of the LOADED_IMAGE structure and 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT) are in use. IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE is set or cleared by using the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE linker option.
4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications. Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT.
Limits on physical memory for 32-bit platforms also depend on the Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows 32-bit Windows systems to use more than 4 GB of physical memory.
Memory and Address Space Limits
The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Unless otherwise noted, the limits in this table apply to all supported releases.
| Memory type | Limit on X86 | Limit in 64-bit Windows | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User-mode virtual address space for each 32-bit process | 2 GB Up to 3 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and 4GT | 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared (default) 4 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| User-mode virtual address space for each 64-bit process | Not applicable | With IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set (default): x64: WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB x64: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB Intel Itanium-based systems: 7 TB 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kernel-mode virtual address space | 2 GB From 1 GB to a maximum of 2 GB with 4GT | WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paged pool | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with Service PackВ 1 (SP1), the paged pool can also be limited by the PagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server and Windows ServerВ 2003: 530 MB WindowsВ XP: 490 MB | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: 128 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonpaged pool | 75% of RAM or 2 GB, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space and physical memory. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, the nonpaged pool can also be limited by the NonPagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 256 MB, or 128 MB with 4GT. | RAM or 128 GB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM) WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7 and Windows ServerВ 2008: 75% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB WindowsВ Vista: 40% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System cache virtual address space (physical size limited only by physical memory) | Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space or the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, system cache virtual address space can also be limited by the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 860 MB with LargeSystemCache registry key set and without 4GT; up to 448 MB with 4GT. | Always 1 TB regardless of physical RAM WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 1 TB depending on configuration and RAM. Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 10.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2016.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 8.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2012. Windows ServerВ 2012 is available only in X64 editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 7.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 is available only in 64-bit editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008. Limits greater than 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows VistaThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ Vista.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home ServerWindows Home Server is available only in a 32-bit edition. The physical memory limit is 4 GB. Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003В R2. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 2 (SP2). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 1 (SP1). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows XPThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ XP.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows EmbeddedThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Embedded.
How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limitsDevices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions. Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can. X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the «lost» memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk. Adblockdetector |